On 30th June, 2020 IBM officially launched the latest DB2 release, DB2 Nebula 11.5.4. The Triton midrange team has been exploring some of the exciting features that the new DB2 release has to offer. In this series we take a look at our DB2 11.5.4 feature highlights and include our initial first impressions.
In the fourth in our series Iqbal Goralwalla looks at DB2 Graph.
DB2 Graph
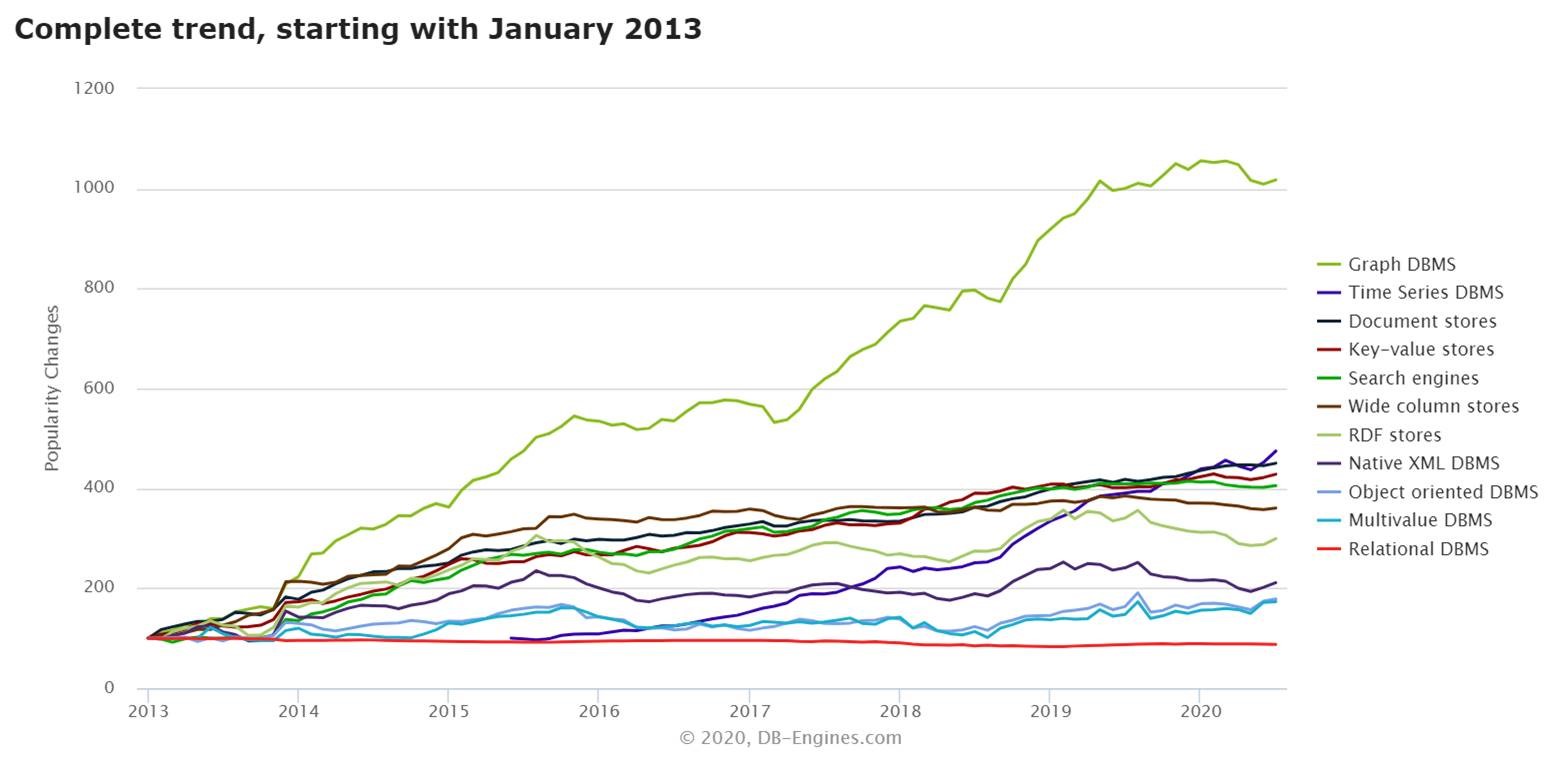
Graph and network data created by modern applications such as social networks, asset management, fraud detection has seen an exponential rise in recent years. Finding insights into this data is becoming increasingly important. Specialised graph databases are becoming increasingly popular to address the challenge in analysing this data and finding relevant insights. This is clearly seen in the following chart (taken from https://db-engines.com/) showing the historical trend of database popularity.
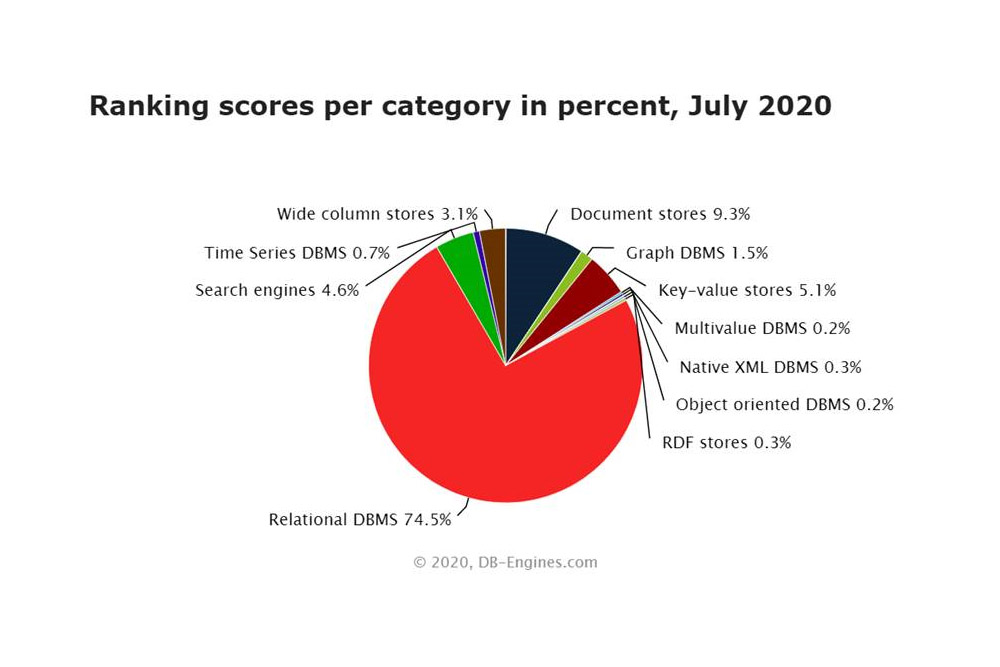
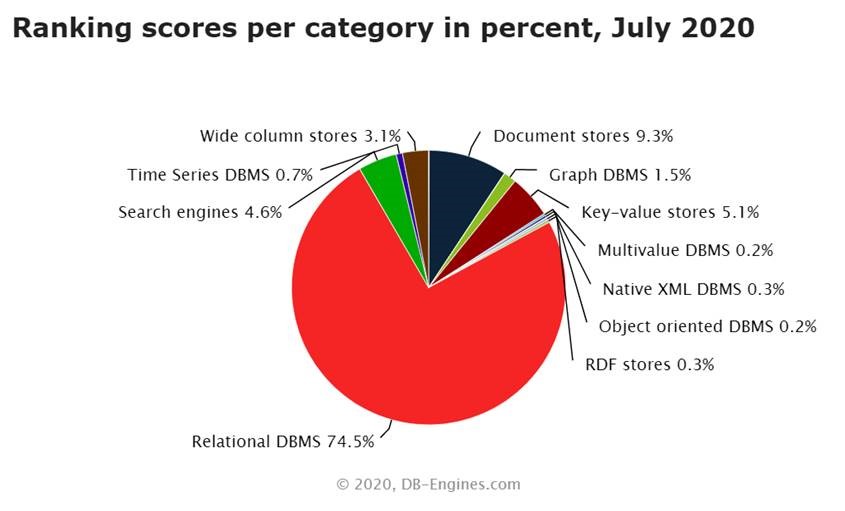
However, a large number of modern applications still store data in relational databases. More than 70% to be more specific as seen in the following chart (taken from https://db-engines.com/).
I was in conversation recently with a potential customer who have a specialised graph database to help perform fraud analytics. Data is fed into the graph database using an ETL process involving a large amount of data from a DB2 database. And we all know the problems with maintaining and keeping two sets of data. Duplication with associated costs, maintenance, latency, to a name a few. And I thought, since the graph data is actually available in DB2, albeit not stored explicitly as graphs, wouldn’t it be great if we could perform graph analytics within DB2 itself with a comparable performance to a standalone graph database. Real-life, mission critical analytic workloads however, are seldom homogeneous. They include SQL, graph, and other analytics. Although specialised graph databases handle graph analytics very well, they do not perform as well with other analytics. What is needed is a happy marriage between relational and graph analytics.
Well, walls (DB2 development lab in this case!) have ears they say and my thoughts have been answered. DB2 Graph is now available as a Technology preview in DB2 11.5.4, and lets you run gremlin queries on your existing relational database to perform graph analytics without requiring any changes to the underlying database structure. Gremlin queries are transformed and optimised into SQL statements, which get efficiently processed in the DB2 database. I am looking forward to putting DB2 Graph to test and reporting back my findings. So, watch this space.